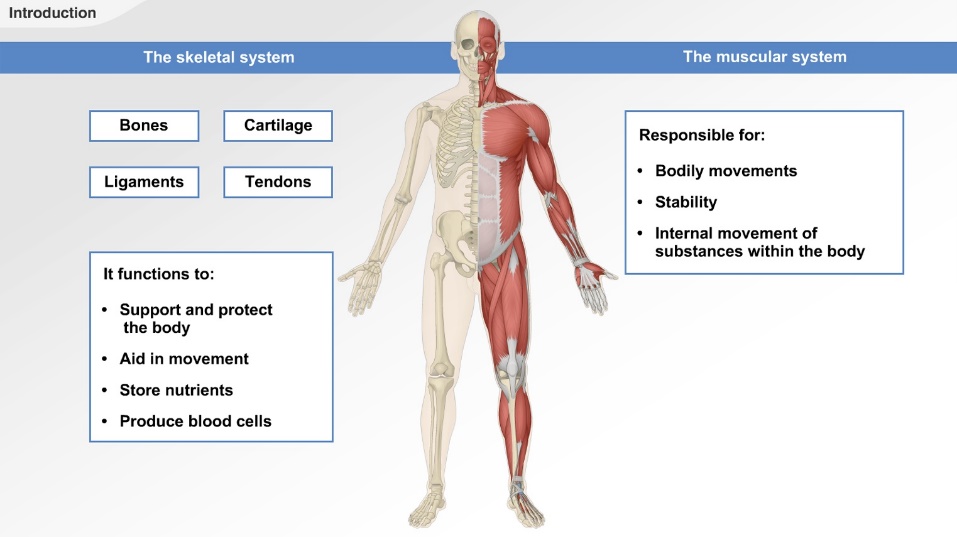
The musculoskeletal system is composed of two systems – the muscular system and the skeletal
system because of the main common functions of the two systems are movement and support.
Primarily, the roles of the musculoskeletal system are movement and support, but the system also
performs the following functions:
- Protection of vital structures
- Provision of body forms
- Stability
- Storage of salts (e.g., calcium)
- Formation and supply of new blood cells.
Human skeletal system
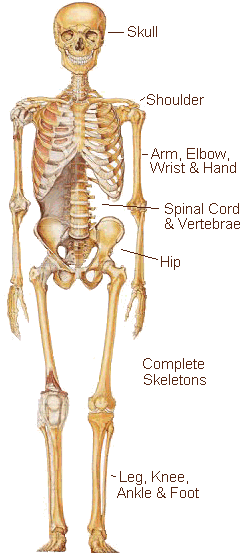
Bone, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the
support structure of the body. In the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the rib
cage and joints), cartilage, a semi-rigid form of connective tissue, provides flexibility and smooth
surfaces for movement. The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and
performs the following critical functions for the human body:
- supports the body
- facilitates movement
- protects internal organs
- produces blood cells
- stores and releases minerals and fat
Human Muscular system
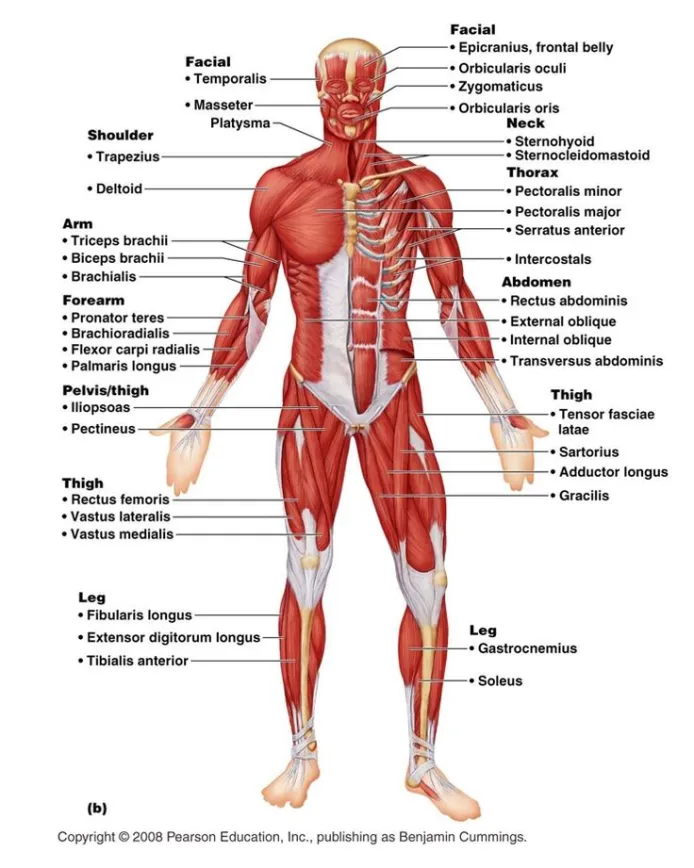
The muscular system is comprised of the sum total of muscles throughout the body that move the skeleton, maintain posture through steady contraction, and generate heat through cell metabolism. Humans have three types of muscle.
There are three types of muscle tissue:
Skeletal muscle
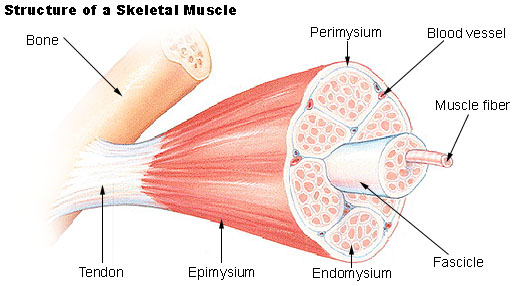
- This type of muscle creates movement in the body. There are more than 600 skeletal muscles, and they makes up about 40 percent of a person’s body weight.
- When the nervous system signals the muscle to contract, groups of muscles work together to move the skeleton. These signals and movements are nearly involuntary, yet they do require conscious effort.
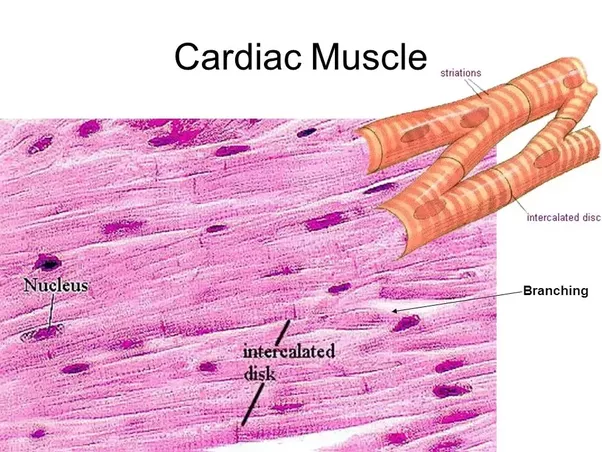
Cardiac Muscle
- Cardiac muscle is involuntary muscle. This type makes up the walls of the heart and creates the steady, rhythmic pulsing that pumps blood through the body from signals from the brain. T
- This muscle type also creates the electrical impulses that produce the heart’s contractions, but hormones and stimuli from the nervous system can also affect these impulses.
Smooth muscle
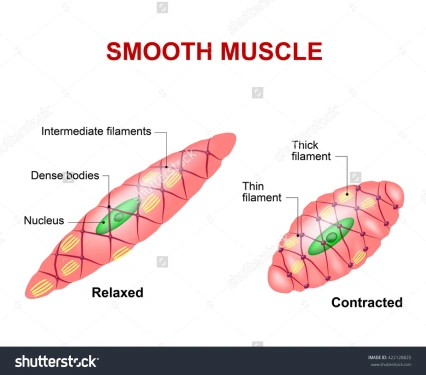
- Smooth muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs, respiratory passageways, and blood vessels. Its wavelike movements propel things through the bodily system, such as food through your stomach or urine through your bladder.
- Like cardiac muscle, smooth muscle is involuntary and also contracts in response to stimuli and nerve impulses.
