
Mastectomy is the removal of the whole breast. Mastectomies are primarily performed to remove or prevent breast cancer.
Why do we perform Mastectomy?
Mastectomies are used for Following cancerous and non cancerous conditions :
- Non-invasive breast cancer – This cancer forms in the milk ducts but has not yet spread out into the rest of the breast tissue.
- Stages 1 and 2 – early stage breast cancer.
- Stage 3 – locally advanced breast cancer (after chemotherapy).
- Inflammatory breast cancer – an aggressive disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast (mastectomy is only suitable after chemotherapy for this form of cancer).
- Paget’s disease of the nipple or breast – a rare type of cancer affecting the nipple.
- Locally recurrent breast cancer – cancer returning to the same breast.
- severe chronic breast pain
- fibrocystic breast disease
- dense breast tissue
- cancer phobia or a family history of breast cancer.
Types of mastectomy
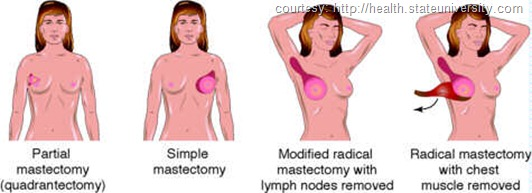
Total (simple) mastectomy
- The surgeon removes the entire breast.
- The surgeon does not perform axillary lymph node dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the underarm area). Sometimes, however, lymph nodes are occasionally removed because they happen to be located within the breast tissue taken during surgery.
- No muscles are removed from beneath the breast.
Note: A simple or total mastectomy is appropriate for women with multiple or large areas of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and for women seeking prophylactic mastectomies — that is, breast removal in order to prevent any possibility of breast cancer occurring.
Double mastectomy
Both breasts are removed as a preventive measure; this is often used for high-risk patients who have specific genetic markers that make breast cancer more likely.
Radical mastectomy
The entire breast, underarm lymph nodes, and chest wall muscles are removed.
Note: Radical mastectomy is recommended only when the breast cancer has spread to the chest muscles under the breast. Radical mastectomy is now rarely performed because in most cases, modified radical mastectomy has proven to be effective.
Modified radical mastectomy
The entire breast and underarm lymph nodes are removed, but the chest wall muscles are left intact.
Note: People with invasive breast cancer who decide to have mastectomies will receive modified radical mastectomies so that the lymph nodes can be examined. Examining the lymph nodes helps to identify whether cancer cells may have spread beyond the breast.
Skin-sparing mastectomy
The breast tissue and nipple are removed, but the skin is left to reconstruct the breast in the same operation.
Nipple-sparing mastectomy
During nipple-sparing mastectomy, all of the breast tissue is removed, but the nipple is left alone.
Mastectomy with and without breast reconstruction
- If patient choose to have breast reconstruction to help restore the look of the breast that was removed. Reconstruction may be done at the same time as the mastectomy (immediate With CPT 19340) or later (delayed CPT 19342).
- If patient choose immediate reconstruction, surgeons may use a special skin-sparing technique during the mastectomy. That saves much of the skin of the breast. The plastic surgeon can use this skin as an envelope to help form the reconstructed breast.
- Some women choose not to have reconstructive surgery or to do it later.When no reconstruction is planned, the surgeon will leave the area as flat as possible so a breast prosthesis can be comfortably fitted to the chest.
Breast prosthesis
If patient don’t want to have reconstruction, Then breast prosthesis is better option. This is a breast form made of silicone gel, foam or other materials that is fitted to chest.
Coding Guidelines
The pivot of coding mastectomy procedures is the amount of tissue removed and any other tissue that may be removed along with breast tissue.
![]() Mastectomy for gynecomastia — This procedure is performed for treatment of gynecomastia. Gynecomastia is an abnormal condition of large breasts in males. In this procedure, the excess breast tissue is removed. Use code 19300 to report mastectomy for gynecomastia. This is a gender specific code and should be coded for male patients only.
Mastectomy for gynecomastia — This procedure is performed for treatment of gynecomastia. Gynecomastia is an abnormal condition of large breasts in males. In this procedure, the excess breast tissue is removed. Use code 19300 to report mastectomy for gynecomastia. This is a gender specific code and should be coded for male patients only.
![]() Partial Mastectomy – also known as lumpectomy, tylectomy, quadrantectomy and segmentectomy.
Partial Mastectomy – also known as lumpectomy, tylectomy, quadrantectomy and segmentectomy.
- If the procedure is performed without axillary lymphadenectomy, then report with code 19301.
- If the axillary lymph nodes are removed along with the tumor, adequate normal breast tissue around the tumor, skin and lining of chest muscle then report with code 19302. .Do not report 19302 for removal of a few nodes. Further, code 19302 involves removal of lymph node between the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles and axillary nodes.
![]() Simple Complete Mastectomy — Total mastectomy, this procedure involves removal of entire breast tissue, leaving the lymph nodes and surrounding muscle intact. Report with code 19303 for a simple total/complete mastectomy.
Simple Complete Mastectomy — Total mastectomy, this procedure involves removal of entire breast tissue, leaving the lymph nodes and surrounding muscle intact. Report with code 19303 for a simple total/complete mastectomy.
![]() Subcutaneous Mastectomy — Also called nipple sparing mastectomy. As the name suggests, this procedure involves removal of the entire breast tissue under the skin. The nipple and overlying skin is left intact. Report with code 19304 for a subcutaneous mastectomy.
Subcutaneous Mastectomy — Also called nipple sparing mastectomy. As the name suggests, this procedure involves removal of the entire breast tissue under the skin. The nipple and overlying skin is left intact. Report with code 19304 for a subcutaneous mastectomy.
![]() Radical Mastectomy
Radical Mastectomy
- Removal of entire breast tissue, axillary lymph nodes, pectoral muscle and surrounding fatty tissue. Report with code 19305 for radical mastectomy including pectoral muscle and axillary lymph nodes.
- Removal of entire breast tissue, skin, axillary lymph nodes, internal mammary nodes and pectoral muscle. This type of mastectomy is also referred to as Urban operation. Report with code 19306 for radical mastectomy including pectoral muscle, axillary and internal mammary lymph nodes.
![]() Modified Radical Mastectomy — This procedure involves removal of entire breast tissue (skin, areola, nipple), and axillary lymph nodes. The pectoralis minor muscle may or may not be removed; however, the pectoralis major muscle is not removed. Report with code 19307 for modified radical mastectomy including axillary lymph nodes, with or without pectoralis minor muscle but excluding pectoralis major muscle.
Modified Radical Mastectomy — This procedure involves removal of entire breast tissue (skin, areola, nipple), and axillary lymph nodes. The pectoralis minor muscle may or may not be removed; however, the pectoralis major muscle is not removed. Report with code 19307 for modified radical mastectomy including axillary lymph nodes, with or without pectoralis minor muscle but excluding pectoralis major muscle.
Important Point
- Mastectomy procedures are unilateral procedures. To report bilateral performance, add modifier 50.
- Codes 38500, Biopsy or excision of lymph node(s); open, superficial and 38525, Biopsy or excision of lymph node(s); open, deep axillary node(s) should be reported for removal/sampling of few sentinel nodes without complete axillary dissection.
Example: A patient undergoes partial mastectomy of right breast for treatment of localized lesion suspected to be malignant. The physician removes three superficial sentinel nodes using an open approach. In this case, codes 19301- RT and 38500 should be reported for right partial mastectomy and removal of superficial sentinel nodes respectively.
- Reporting of axillary lymph node dissection during partial mastectomy (code 19302) does not depend on the incision made for axillary dissection but the extent of axillary node dissection. Axillary dissection through the same incision as partial mastectomy or through a different incision does not make any difference in the choice of code.
- Placement of fiducial marker is inclusive to code 19301, Mastectomy, partial (eg, lumpectomy, tylectomy, quadrantectomy, segmentectomy).
